The Recursive Model & Finite Math Exercises
Unit 3: Looking Forward
This unit builds on the analysis of past distributions in deriving estimates of future counts. Students are challenged in each lesson to explain possible reasons behind each new iteration of a population projection model (for example, a war or economic conditions that impact immigration or changes in birth rates). The unit begins by developing an arithmetic sequence based on the 2010 and 2015 population totals. Lesson 8 summarizes this sequence with a linear model used to estimate the future population totals. A geometric sequence is used to derive an exponential model in Lesson 9. Each of these lessons, however, does not obtain estimates for the age groups. Although it is possible to derive age group estimates using these models, the age group analysis begins in Lesson 10 with the special recursive model designed for this module.
Lesson 10 introduces an important feature of the recursive model identified as population factors. Applying these factors to build estimates of future age groups is done in Lesson 11.
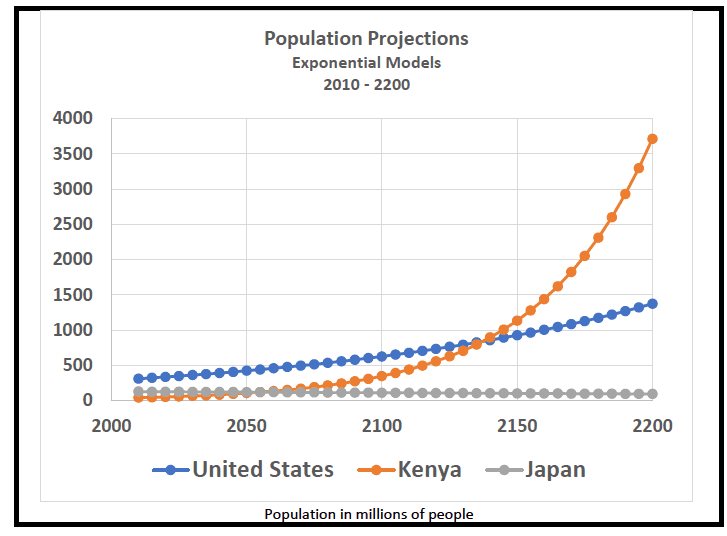
Lesson 12 completes the recursive model by developing foundation factors that fill in the “hole” left by the 0-4-year-old age group in each iteration. As this hole is derived, the resulting projections based on population factors are completed. Lesson 13 and Lesson 14 build off these estimates to summarize the shapes and projected changes in the population of the United States, Kenya, and Japan.
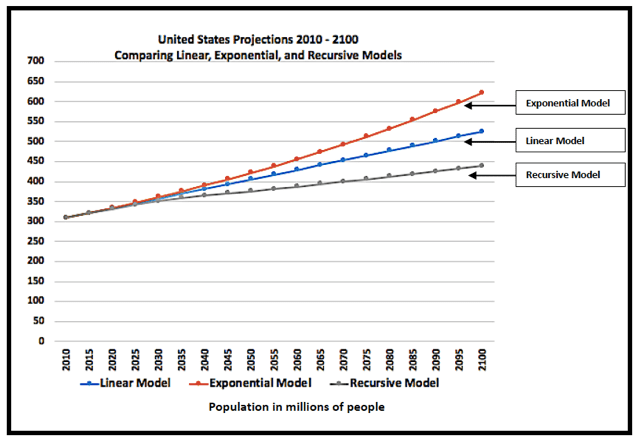
Students derive and graph linear and exponential projections of future population distributions. Each distribution is a preview of the more detailed model identified as the recursive model.
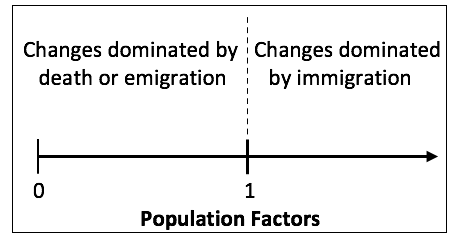
Critical components of the recursive model are two factors. The first factor (defined as the population factor) is derived and analyzed for each 5-year age group of the population distribution. This factor indicates population changes for each 5-year age group as either dominated by immigration or death and emigration.